Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
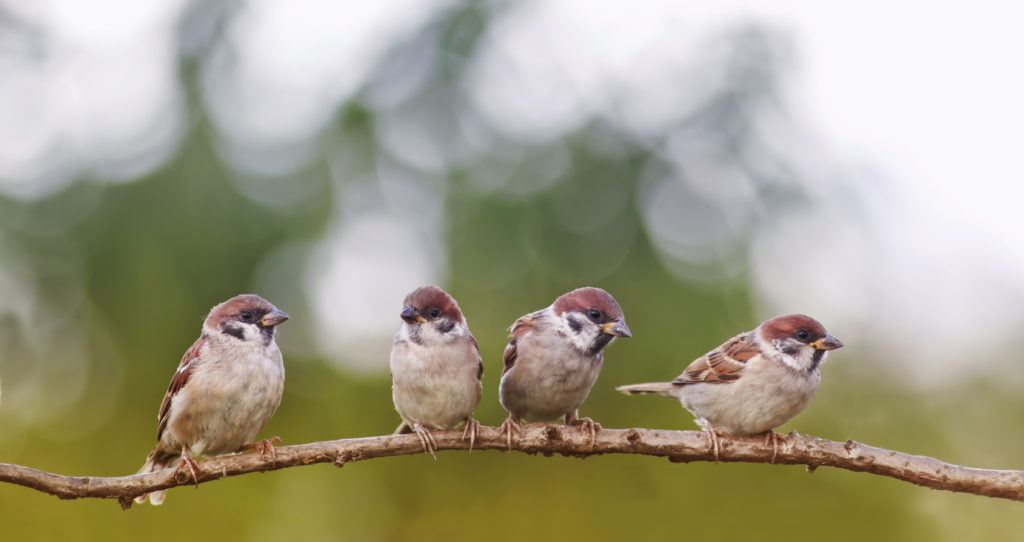

Waking up to an early morning chorus of birdsong is nice. No doubt about that. But the benefits could be much more significant than just a fleeting feeling of positivity (and followed by a groan to get out of bed by some).
Researchers at Kings College London have just reported on the results of a study that tracked people’s exposure to birdsong and the resulting mental health impact – with some very positive results.
Hammoud et al. tracked 1’292 participants over three years who completed an impressive 26’856 assessments. They used an app that asked them three times a time whether they could hear birdsong and then followed up with questions on mental health.
What did they find?
They found that seeing or hearing birds was associated with an improvement in wellbeing and that this can last up to eight hours. Not bad for a bit of birdsong. What’s more they also found that this also improved wellbeing in those suffering from depression.
This supports plenty of other research into the benefits of nature and specifically of just birdsong. I reported on the positive effects of biodiversity and birdsong here. But these researchers were also able to account for co-occurring other environmental factors such as seeing tress – we also know greenspace has a positive benefit – and found that birdsong alone could account for positive benefits.
So, that’s all good news – surprising and effective method to improve mental wellbeing – so open the windows and listen to the birds. It will do you good.

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker, speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
References
Ryan Hammoud, Stefania Tognin, Lucie Burgess, Nicol Bergou, Michael Smythe, Johanna Gibbons, Neil Davidson, Alia Afifi, Ioannis Bakolis, Andrea Mechelli.
Smartphone-based ecological momentary assessment reveals mental health benefits of birdlife.
Scientific Reports, 2022; 12 (1)
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-20207-6
More Quick Hits
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...