Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences

Love and kindness
We all know that some people are more altruistic than others. Most of us will also admire acts of selfless behaviour. The hero who saves a person, the people who serve others tirelessly on various volunteer projects, and those kind people who always seem to have time to help another soul.
So, if we know some people are more altruistic, it would follow that we should be able to see this in a brain. Some regions have been identified as helping with various social skills such as the medial frontal cortex (I review psychopaths in this article and their brains – the opposite of altruists).
However, a group of researchers at Birmingham University have now been able to identify another region of the brain that seems to be specifically involved when making conscious, and effortful, decisions to help others. This activates differently to decisions to help oneself.
What did these researchers discover?
Patricia Lockwood et al. worked with 38 people between 18 and 35. They took part in effortful decision-making tasks, self-assessed their empathy, and went through a series of decisions while having their brains scanned. In this particular experiment the particularly clever bit was that the candidates had to work. This is a problem of brain scanning. It can’t be done in the real world or when walking around – only lying in a scanner. This means that decisions can be made but that may not reflect the amount of effort a person will invest into a task.
In this experiment participants had to squeeze a device that measured grip strength – they had to squeeze hard enough and long enough to reach a threshold to get a reward. The researchers could therefore see how much effort a person was willing to exert to get various rewards. But in this case, they could also see and accurately measure differences for work to get a reward for oneself or work done to get a reward for another person. Ingenious.
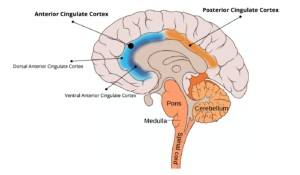 And in doing this they managed to identify a region called the anterior cingulate cortex gyrus (ACCg) that was associated with the effortful decision.
And in doing this they managed to identify a region called the anterior cingulate cortex gyrus (ACCg) that was associated with the effortful decision.
- Firstly, it did not activate when making an effortful decision for themselves.
- Secondly those who said they were more altruistic also had the strongest effort patterns in the ACCg.
- Thirdly stronger grip activation was associated with stronger activation of the ACCg suggesting that this region directly correlates with effortful decision to help others.
As usual for this kind of study a lot more work has to be done with different individuals and also, for example, with those who have antiscoail perosnality disorder or psychopaths.
Nevertheless, a fascinating piece of research, particularly when we consider that the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (for review see here) has multiple associations with decision-making, error detection, but also with behaviour change. So, it looks promising.
Can we train the ACCg? Unlikely, but having this knowledge is still likely to be useful.
And I certainly feel my ACCg seems to be in good shape!

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker, speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Patricia L. Lockwood, Marco K. Wittmann, Hamed Nili, Mona Matsumoto-Ryan, Ayat Abdurahman, Jo Cutler, Masud Husain, Matthew A.J. Apps.
Distinct neural representations for prosocial and self-benefiting effort.
Current Biology, 2022
DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.08.010
More Quick Hits
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...