Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
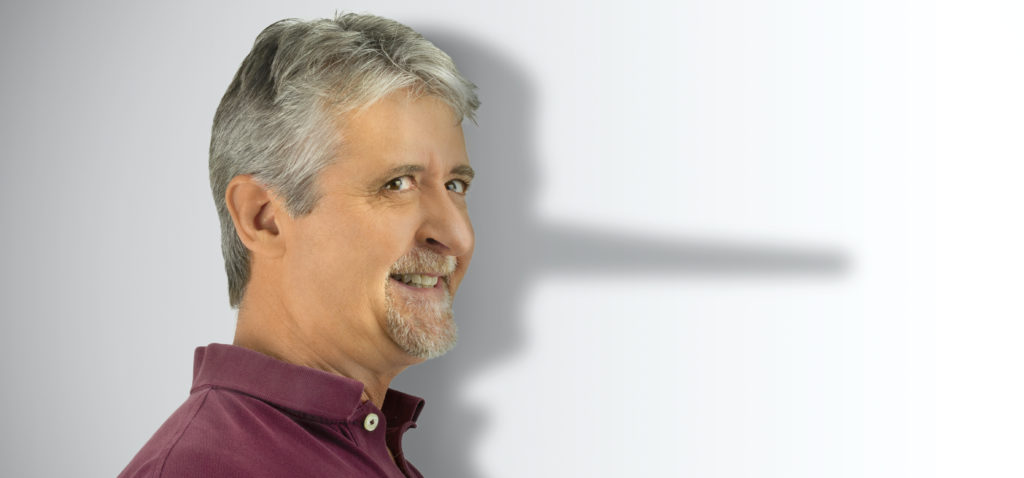

The one place that we can consistently catch people lying is in job interviews. And the question has long been how do you catch out these liars? The answer is you need to outsmart them.
But how?
Well lying uses cognitive resources. It is effortful because you have to construct an alternative narrative in your head and then keep this in your mind as you answer questions on this, or questions related to this. It is an effortful process. Therefore, if you can disrupt this process, you can uncover the liars.
Professor Aldert Vrij, from the Department of Psychology at the University of Portsmouth used this principle to design an experiment to outsmart liars. The way he did this is to give interview participants a cognitive task – this cognitive task means participants need to use cognitive resources and so this makes it much more difficult to tell a convincing lie and stick to this accurately.
The experiment had participants interviewed about societal topics, but they were instructed to either represent their own honest views or to lie about their views. They were also given time to prepare for this interview, giving them the ability to prepare elaborate and convincing lies. They were also incentivised by being entered into a prize draw. However, they were also given a 7-digit license plate number to remember. And some were told that if they failed to remember this, they would have an additional task of writing down their opinions after the interview.
What were the results?
They found that the additional cognitive tasks made the liars stories less plausible but, interestingly, only if this was considered important. This shows that if it is not considered important, they do not commit the cognitive resources to it, and so can lie more effectively.
So, to catch out liars you need to give them cognitive tasks that they will engage in, and this will inhibit their ability to construct plausible lies.
This can be done in interviews but may be a problem in every day life!●

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Aldert Vrij, Haneen Deeb, Sharon Leal and Ronald P. Fisher.
The Effects of a Secondary Task on True and False Opinion Statement.
International Journal of Psychology & Behavior Analysis, 2022
DOI: 10.15344/2455-3867/2022/185
More Quick Hits
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...