Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
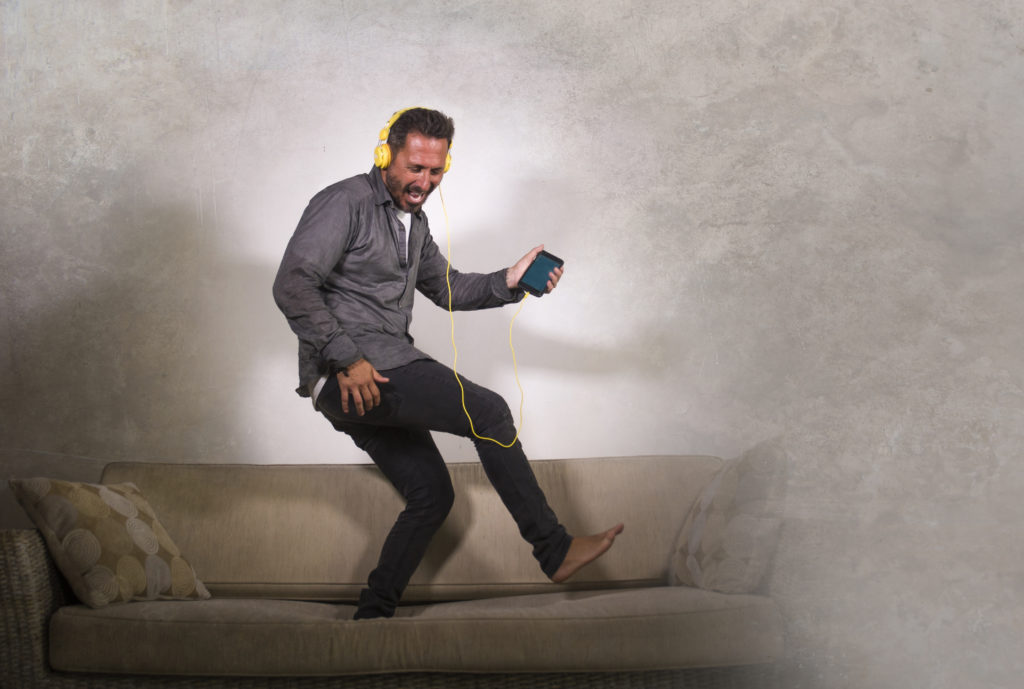

Get into the groove… or so sang Madonna with her hit single in 1985. Little did she know at the time but getting into the groove certainly does seem to be beneficial for you – not to prove your love as she demanded, but in improving cognitive, brain, performance.
Really, yes.
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba in Japan have investigated the impact of groovy music, music related to rhythm and dance, and stimulating the urge to move, on cognitive performance.
To do this these researchers gave cognitive tasks and conducted brain scans using near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) to measure participants before and after playing groovy music.
They found that groovy music improved cognitive performance scores, and this was related to increased function in an area of the brain called the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (l-DLPFC). Many prefrontal regions are associated with higher cognitive functions. However, there is a caveat, and that is this effect could only be seen in those participants who said they enjoyed the music only.
So, this raises the question of whether it is groovy music that stimulated this process or simply music that you enjoy – other research has shown the positive benefits of music on just about everything.
So, for you groovers, music that makes you want to move your body, to groove, is likely good for your brain performance. If you don’t like the groove, you can certainly try with any music you like. It will at least elevate your mood and that in itself is no bad thing.

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Takemune Fukuie, Kazuya Suwabe, Satoshi Kawase, Takeshi Shimizu, Genta Ochi, Ryuta Kuwamizu, Yosuke Sakairi, Hideaki Soya.
Groove rhythm stimulates prefrontal cortex function in groove enjoyers.
Scientific Reports, 2022; 12 (1)
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11324-3
More Quick Hits
Your brain on near-death experiences
Near-death experiences have fascinated many people ever since they have been reported. And these experiences guide our view of how we die: the memories of your life passing in front of your eyes, the tunnel of light, the floating movement towards a bright light....
Social networks grow your brain
The headline is a bit “click baity” but it is what a group of researchers found. To be more specific they found in macaques (cute monkeys) in the wild that having more grooming partners grew different regions of the brain. Grooming is the primate version of having a...
What do creative brains look like?
We’d probably all be happy to be a bit more creative — though research into our own opinions show that many people do actually consider themselves to be above average in creativity. An obvious self-bias. This is where scientists who study creativity come in and find...
New gender biases discovered
There have been many studies on gender biases, and I have followed, written, and spoken about many of these biases over the years (over a decade actually) but two studies have just come out that caught my eye. One out of New York University focused on gender natural...
Growth of your brain over your life
So, we all know that our brain grows very quickly as babies and children and then after a certain age, younger than some of us may like to think, there begins a slow decline. But precisely what and how is the question. Well, this is a question that an international...
How to reduce loneliness
I have reported multiple times on loneliness during the pandemic – mostly because interest and research into loneliness has taken a large uptick. I have also reported on how to combat this and was happy to see that a piece of research just out proved what I had...