Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
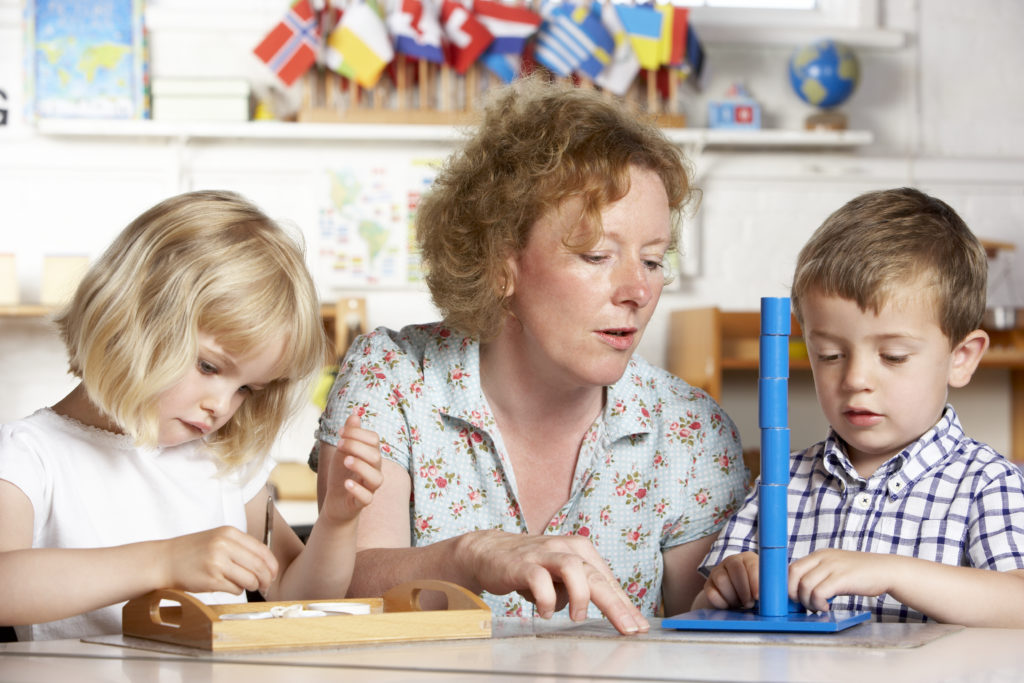

Good news for some and bad news for traditionalists in education.
Some believe that starting education early and using classical and traditional learning activities is the best way to develop children and their brains. Though we do know that early education can be surprisingly important – as I reported here with results seen in the brain up to 40 years later – but we also know that things like simply playing can be beneficial to children.
This is because play in itself uses multiple cognitive resource and often in complex ways and so can be more than beneficial than some schooling approaches. This is in contrast to passive activities such as watching television or engaging in most of social media.
This review out of the University of Cambridge looked at a total of 39 studies including over 3’800 children between three and eight and asked the question of whether guided play could be as effective as traditional approaches to learning. Guided play allows children to engage in playful activities but are guided and prompted by the teacher in certain directions.
What was the result?
The results were positive – very positive. Remember this was a large-scale analysis and they also measured comparative effects by consolidating results from multiple other studies. This was then translated into a relative effect.
In maths ability there was a small comparative positive effect. This shows that guided play was generally more effective than traditional methods and in other areas, shape knowledge, for example, the effect was much larger. There was also evidence that guided play improved the cognitive ability to switch between tasks.
All in that is already a very good result showing that guided play was more effective on average than traditional instruction. But the authors also note multiple other benefits that guided play may include but weren’t measured directly in this study. This includes motivation, persistence, creativity, and confidence. All in that paints a very positive picture for the use of guided play!
So what are you, or rather parents, teachers, and educational authorities, waiting for?
And what about in adults? I suspect I already know the answer to that!

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Kayleigh Skene, Christine M. O’Farrelly, Elizabeth M. Byrne, Natalie Kirby, Eloise C. Stevens, Paul G. Ramchandani.
Can guidance during play enhance children’s learning and development in educational contexts? A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Child Development, 2022;
DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13730
More Quick Hits
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...