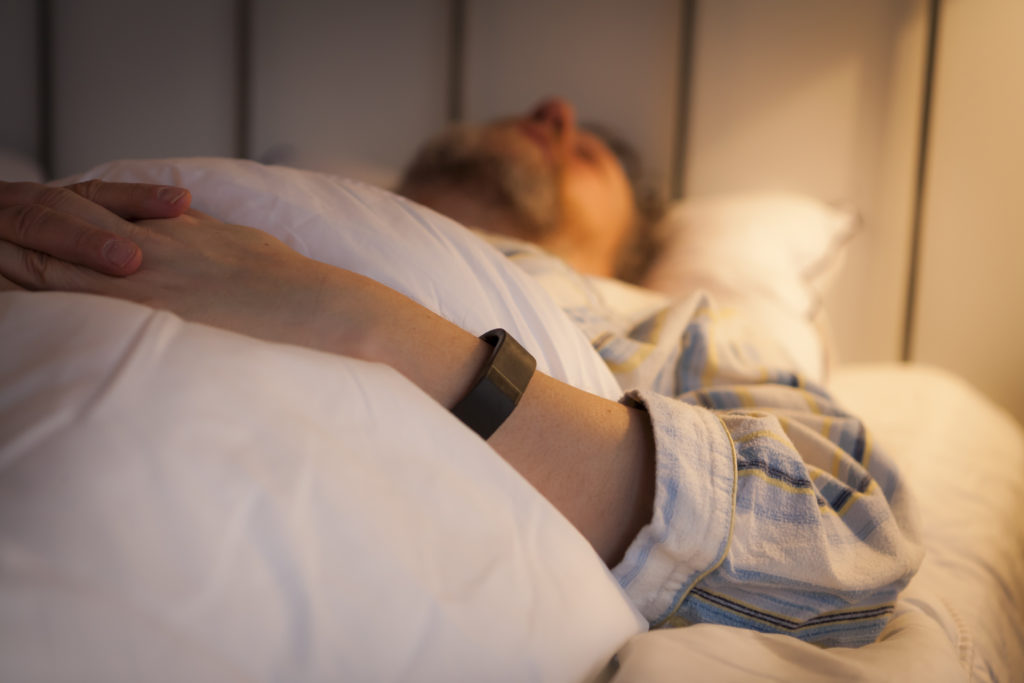
I’ve reported multiple times on sleep and how it affects just about everything form cognitive performance, to brain plasticity, to physical performance, to mental health, and to metabolism.
The question that remains open is, however, how much sleep is ideal? The old advice of eight hours is pretty close to the truth, but it also changes over lifetimes. We all know that babies need a lot more sleep, for example. Teenagers also seem to sleep a lot.
Research into pre-industrial societies showed, what was surprising at the time, that they don’t sleep as much as many had thought, normally between six and eight hours a night on average.
In comes this recent study out of the University of Cambridge. They analysed data from almost 500,000 people between the ages of 38 and 73. These were asked about their sleep patterns, mental health, and wellbeing, and also took cognitive tests. There was brain imaging and genetic data available for about 40,000 of these participants. That’s a pretty impressive dataset!
We have known for a long time that too little sleep impedes cognitive performance and can lead to multiple negative health impacts. However, what was surprising about this data is that it showed that too little or too much sleep had similar impacts. That is, reduced cognitive performance, more anxiety, increased symptoms of depression, and worse wellbeing overall. They also found links to the size of brain areas associated with cognitive performance
What was the ideal amount of sleep? It was seven hours sleep.
However, the researchers also noted that consistency was key – firstly in getting a solid seven hours rather than an interrupted seven hours, and this being consistent from night to night.
I was also relieved to read the above having independently found that 7 hours 15 minutes is my optimal sleep duration and have managed to stick to this consistently in recent years. However, I am trying to catch up on a few decades of sleep abuse also!
Reference:
Yuzhu Li, Barbara J. Sahakian, Jujiao Kang, Christelle Langley, Wei Zhang, Chao Xie, Shitong Xiang, Jintai Yu, Wei Cheng, Jianfeng Feng.
The brain structure and genetic mechanisms underlying the nonlinear association between sleep duration, cognition and mental health.
Nature Aging, 2022
DOI: 10.1038/s43587-022-00210-2
More Quick Hits
Your brain on near-death experiences
Near-death experiences have fascinated many people ever since they have been reported. And these experiences guide our view of how we die: the memories of your life passing in front of your eyes, the tunnel of light, the floating movement towards a bright light....
Social networks grow your brain
The headline is a bit “click baity” but it is what a group of researchers found. To be more specific they found in macaques (cute monkeys) in the wild that having more grooming partners grew different regions of the brain. Grooming is the primate version of having a...
What do creative brains look like?
We’d probably all be happy to be a bit more creative — though research into our own opinions show that many people do actually consider themselves to be above average in creativity. An obvious self-bias. This is where scientists who study creativity come in and find...
New gender biases discovered
There have been many studies on gender biases, and I have followed, written, and spoken about many of these biases over the years (over a decade actually) but two studies have just come out that caught my eye. One out of New York University focused on gender natural...
Growth of your brain over your life
So, we all know that our brain grows very quickly as babies and children and then after a certain age, younger than some of us may like to think, there begins a slow decline. But precisely what and how is the question. Well, this is a question that an international...
How to reduce loneliness
I have reported multiple times on loneliness during the pandemic – mostly because interest and research into loneliness has taken a large uptick. I have also reported on how to combat this and was happy to see that a piece of research just out proved what I had...
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...