Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
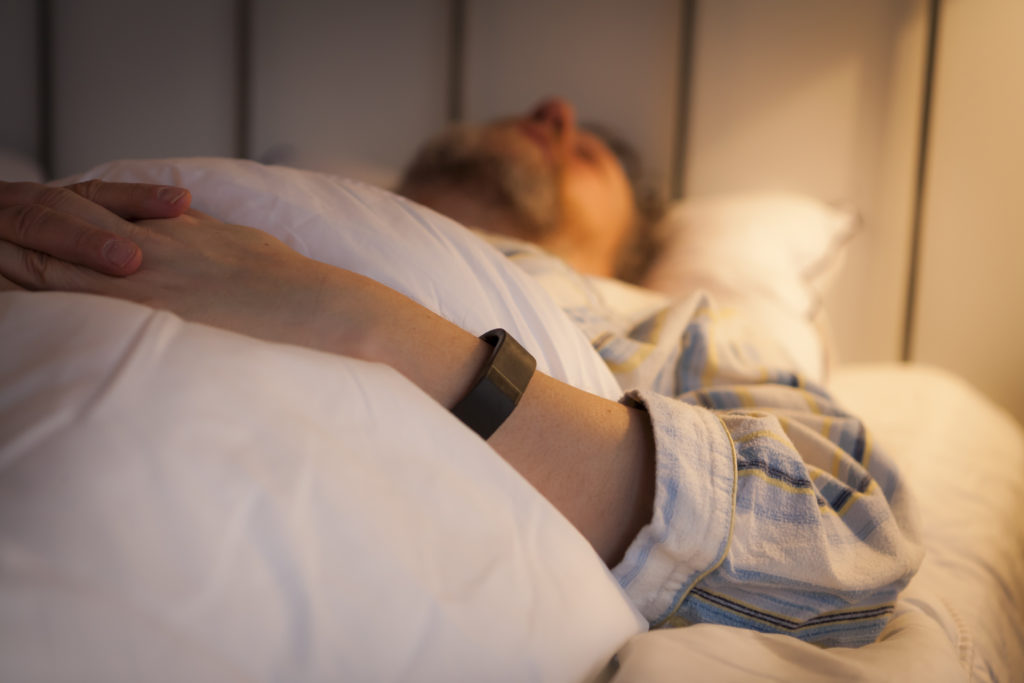

Sleeping well is essential to brain health
Sleep on i” is common advice for many reasons. Often to consolidate thoughts and help boost creativity. This is a well-known effect. We also know that sleep is the time that helps to detoxify and grow the brain and body, and I have reported on some of these effects in different posts. But this latest research, from the University of Bern, here in Switzerland, supports another hypothesis of sleep — namely that it helps with your emotions.
That sleep, particularly REM sleep (REM sleep is the light sleep phases often associated with dreaming), helps consolidate emotions has been long known. But these researchers found out precisely how this happens in brain cells themselves and this is pretty cool, I have to say.
So, what did they find?
First off, these researchers conditioned mice to two signals. One a fear signal and second, a safety signal. These are the two obvious big emotions in terms of survival and something that is present in all species of animal. They were then able to precisely track these signals in the mice.
What they then found during sleep was astonishing. They found that there was decoupling within neurons to these signals. Specifically, the cell body seemed to be deactivated whereas the dendrites the connecting arms of the neurons activated and processing the emotion. This, the researchers note translates into preferential processing in sleep of safety signals and avoidance of overgeneralising fear emotions which can become generalised anxiety — and they suspect potentially lead to anxiety disorders.
So, the brain needs sleep to process emotions and recorrect emotional signalling but specifically the decoupling of brain cells enables the processing of fear without generalising this. Clever old brain cells.
So, another, another, very good reason to get a good night’s sleep. If you are wondering how much — this latest research here answers that.

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Mattia Aime, Niccolò Calcini, Micaela Borsa, Tiago Campelo, Thomas Rusterholz, Andrea Sattin, Tommaso Fellin, Antoine Adamantidis.
Paradoxical somatodendritic decoupling supports cortical plasticity during REM sleep.
Science, 2022; 376 (6594): 724
DOI: 10.1126/science.abk2734
More Quick Hits
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...