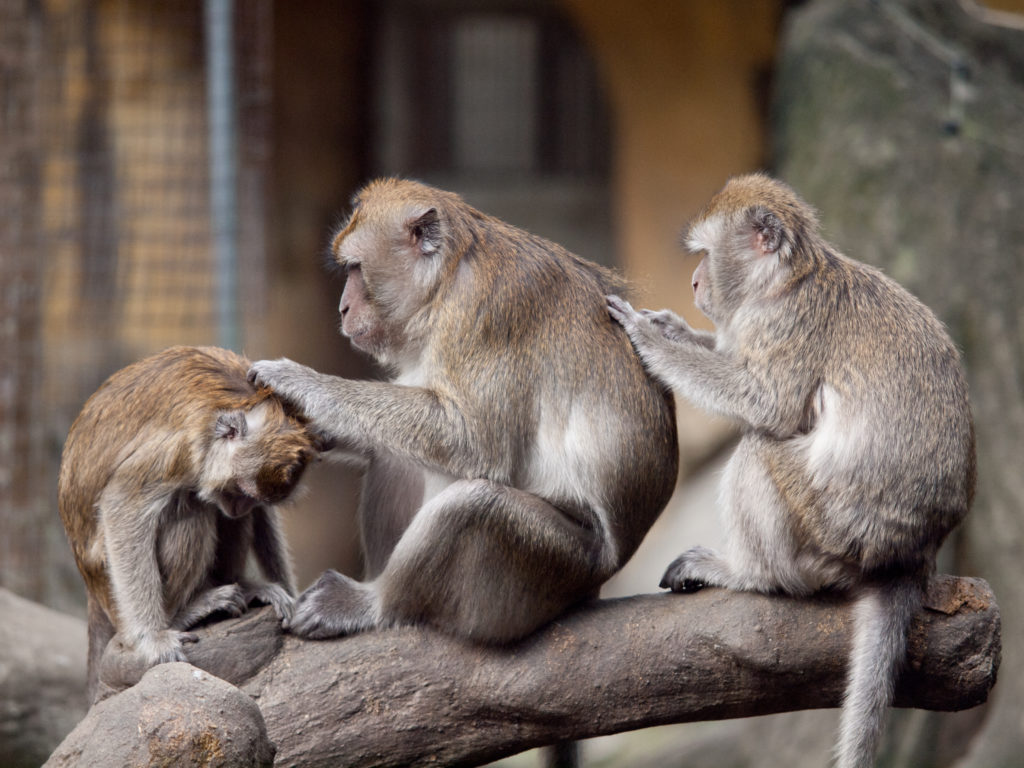
The headline is a bit “click baity” but it is what a group of researchers found. To be more specific they found in macaques (cute monkeys) in the wild that having more grooming partners grew different regions of the brain. Grooming is the primate version of having a heart-to-heart with a friend, or cuddle with your family or romantic partner.
What is interesting in this research is that it tracked this over time and hence also the growth and development of brain regions over time. Previously we have only been able to associate regions of the brain in animal models and human beings that correlate with sociality.
This is all good and well but it doesn’t give us an indication of causation, a chicken or egg problem: are those with enlarged social regions in the brain more social, or does socialising increase the size of these regions?
These researchers have shown for the first time that grooming, which is an intense form of socialising in macaques does actually grow these regions. And what do these regions do?
Well, the regions that grew were those that are specifically associated with social decision-making and empathy (mid-superior temporal sulcus and ventral-dysgranular insula, if you’re interested).
So, in short, or a more correct headline, is that socialising grows the regions of your brain that are involved in social decision making and empathy.
Probably no bad thing to have!
Reference:
Camille Testard, Lauren J. N. Brent, Jesper Andersson, et al.
Social connections predict brain structure in a multidimensional free-ranging primate society.
Science Advances, 2022; 8 (15)
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl5794
More Quick Hits
Why it pays for companies to help workers have a good day in the office
usiness and executives in those businesses are more than keen to get a competitive advantage. To this end they invest heavily in technology and getting the right people to do the job. But, I am sure, we are all more than aware that the work...
Vaccination to Keep Your Memory?
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ho wouldn’t want to keep their memory when aging?! Well, researchers have just announced some promising results in mice enabling them to keep their memories and avoid some of...
Can Having More Children Reduce Cognitive Functioning?
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences aving more children and late life cognition is not something that is generally researched. There are more obvious avenues such as diet, education, exercise, or socio-economic...
How Sleep Helps Your Brain Manage Fear
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences leep on i” is common advice for many reasons. Often to consolidate thoughts and help boost creativity. This is a well-known effect. We also know that sleep is the time that helps to...
Video games can boost children’s intelligence
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ell, this is not the answer many of us would expect, and it goes against other logic of spending more time doing other things such as reading or socialising with friends...
Just how many people get COVID brain?
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences here are many questions still open about COVID and the brain. There is no doubt that long COVID exists, and this can have dramatic impacts on people’s lives. But just how...
Brain networks and losing weight – successfully or not
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences s weight loss all in the mind? Well, with the danger of oversimplifying a complex topic, this latest research shows it is, and shows precisely how and with what networks. So,...
Reversing aging – with poo!
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ho wouldn't want to age better - well the results of an unsual study are in and the results are promising and may make many of you who are aging prick up your ears. The...
Brisk walking slows biological aging
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences f you want to age better, then walk quicker, or those who walk quicker, age slower. That is the result of a recent study of 400,000 UK adults mapped to genetic markers of age...
Learning at double-speed?
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ouldn’t it be great if we could learn things double speed? Well, maybe we can. At least according to a study out of the University of California. During the pandemic many...