Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
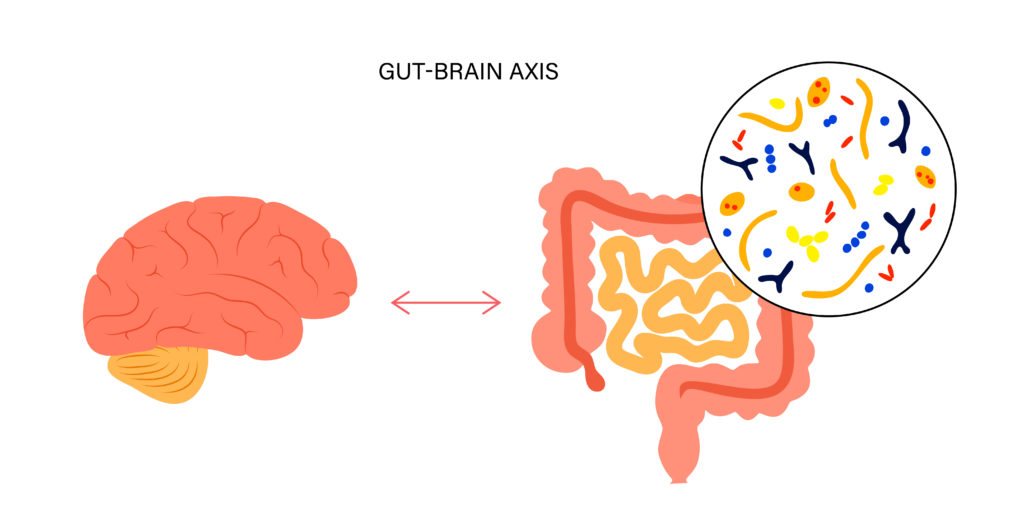
The gut-brain axis
Just after publishing the article on Serotonin and stating that the gut and brain’s serotonin systems can be considered separate entities, out comes a piece of research to show that they are not separate entities.
Indeed, it is known that there is a gut-brain connection that I have also reported on multiple times previously. But researchers are still often in the dark as to how and in what different ways the gut and brain communicate with each other. These researchers at Flinders University developed a new neural tracing technique that helped to investigate this.
They found that the enterochromaffin cells that line the gut and are known to responds to and release neurotransmitters based on stimuli from what is in the gut, communicate to nerve endings. This, through process of diffusion (they are not directly connected to the central nervous system), stimulate pathways that go to the spinal cord and brain.
This therefore strengthens our knowledge of how this happens but also to expand healthcare into more holistic and positive (and potentially more effective and cheaper ways). This suggests, you can eat yourself to better mental health, to a degree at least.

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Kelsi Nicole Dodds, Lee Travis, Melinda A. Kyloh, Lauren A Jones, Damien John Keating, Nick J Spencer.
The gut-brain axis: spatial relationship between spinal afferent nerves and 5-HT-containing enterochromaffin cells in mucosa of mouse colon.
American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 2022;
DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00019.2022
More Quick Hits
Social Interactions Define Your Sense of Purpose
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences aving a sense of purpose is a pretty good thing to have because it seems to correlate with multiple health and life satisfaction measures. If you have a healthy sense of purpose you...
Being “Hangry” Really Is A Thing
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences o, scientists have now proven that being “hangry” is real thing. What took them so long? Well, first of all things which seem intuitively right such as the weather making pain worse...
Reward Drives Aggressive Behaviour Against “Others”
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences s vs. them is known as in-groups vs. out-groups in psychology. This is the well-known effect of people being loyal to their own groups and being competitive and often aggressive to...
Low Oxygen Impairs Decision-Making
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ast year I reported on how pollution and bad air in offices correlates with lower performance and productivity. Something business should take note of. A study out of the University...
The Brain Waves That Drive Social Behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences have reported in other places on the social regions of the brain (for review see here). And this has indeed been the standard approach – try to identify the specific regions in the...
Being Mindful Improves Relationships With Co-Workers
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences he topic of mindfulness has been a hot topic for a number of years now. This is not to be confused with meditation which is often lumped together with mindfulness – because they do...