Quick Hits
Daily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences
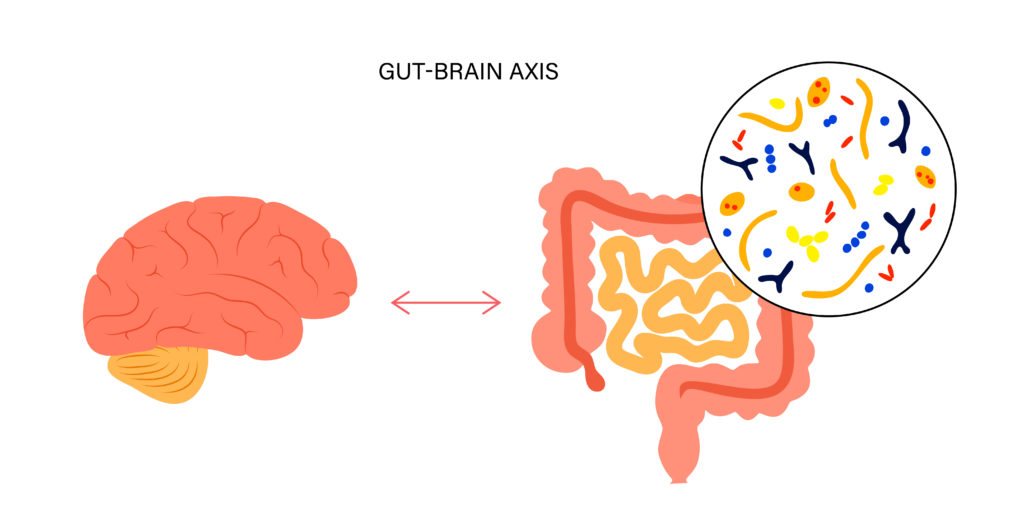
The gut-brain axis
Just after publishing the article on Serotonin and stating that the gut and brain’s serotonin systems can be considered separate entities, out comes a piece of research to show that they are not separate entities.
Indeed, it is known that there is a gut-brain connection that I have also reported on multiple times previously. But researchers are still often in the dark as to how and in what different ways the gut and brain communicate with each other. These researchers at Flinders University developed a new neural tracing technique that helped to investigate this.
They found that the enterochromaffin cells that line the gut and are known to responds to and release neurotransmitters based on stimuli from what is in the gut, communicate to nerve endings. This, through process of diffusion (they are not directly connected to the central nervous system), stimulate pathways that go to the spinal cord and brain.
This therefore strengthens our knowledge of how this happens but also to expand healthcare into more holistic and positive (and potentially more effective and cheaper ways). This suggests, you can eat yourself to better mental health, to a degree at least.

Andy Habermacher
Andy is author of leading brains Review, Neuroleadership, and multiple other books. He has been intensively involved in writing and research into neuroleadership and is considered one of Europe’s leading experts. He is also a well-known public speaker speaking on the brain and human behaviour.
Andy is also a masters athlete (middle distance running) and competes regularly at international competitions (and holds a few national records in his age category).
Reference
Kelsi Nicole Dodds, Lee Travis, Melinda A. Kyloh, Lauren A Jones, Damien John Keating, Nick J Spencer.
The gut-brain axis: spatial relationship between spinal afferent nerves and 5-HT-containing enterochromaffin cells in mucosa of mouse colon.
American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 2022;
DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00019.2022
More Quick Hits
How to reduce loneliness
I have reported multiple times on loneliness during the pandemic – mostly because interest and research into loneliness has taken a large uptick. I have also reported on how to combat this and was happy to see that a piece of research just out proved what I had...
COVID on the Brain
Many COVID-19 patients have reported various neurological symptoms – the well-known brain fog, but also headaches and decreased cognitive function over months and extended periods of time. This even without serious infection or hospitalization. The research seems to...
Life satisfaction after work related to personality traits
As many of you know I have done plenty of work into personality and so found this study interesting. Dusanee Kesavayuth of Kasetsart University in Bangkok, Thailand analysed data from 2,000 adults aged between 50 and 75 in the British Household Panel Survey and found...
Unique regulation of brain in yoga practitioners
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences es, you yoga practitioners knew you were special and here is the science to prove it! In this older study I came across (2018) participants were recruited to see how they dealt with...
Neurodivergence and the lonely brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences eurodivergence is term that describes those that are not “neurotypical” such as those with autism and ADHD. In the surge of research into loneliness spurred by the pandemic it has...
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...