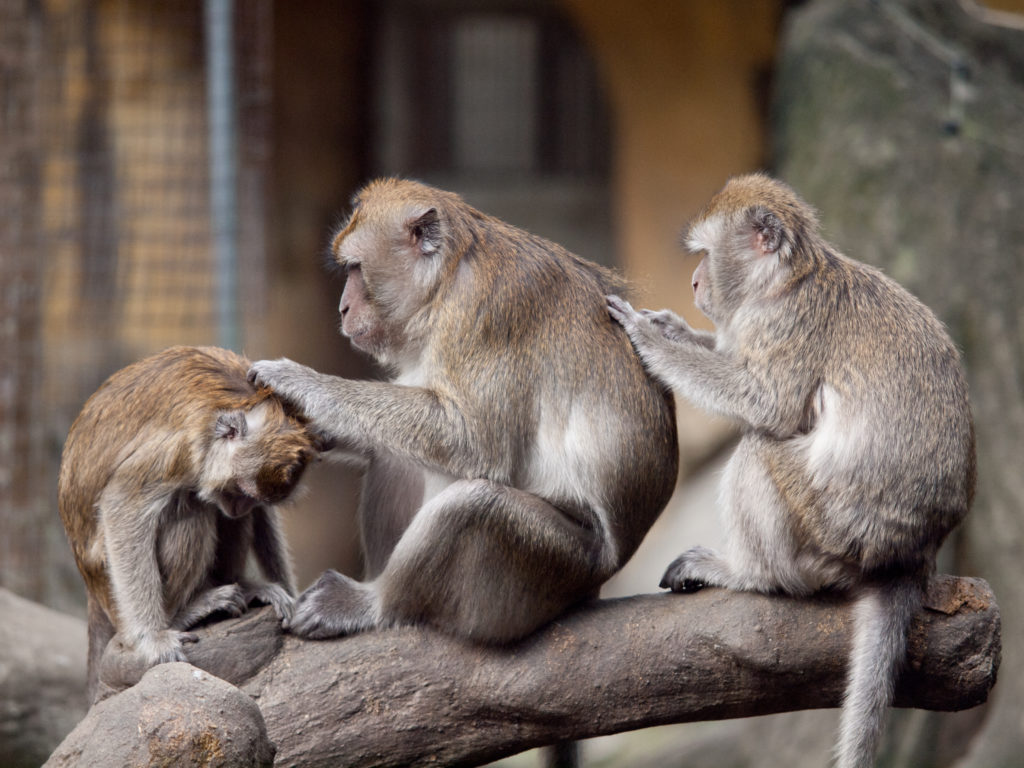
The headline is a bit “click baity” but it is what a group of researchers found. To be more specific they found in macaques (cute monkeys) in the wild that having more grooming partners grew different regions of the brain. Grooming is the primate version of having a heart-to-heart with a friend, or cuddle with your family or romantic partner.
What is interesting in this research is that it tracked this over time and hence also the growth and development of brain regions over time. Previously we have only been able to associate regions of the brain in animal models and human beings that correlate with sociality.
This is all good and well but it doesn’t give us an indication of causation, a chicken or egg problem: are those with enlarged social regions in the brain more social, or does socialising increase the size of these regions?
These researchers have shown for the first time that grooming, which is an intense form of socialising in macaques does actually grow these regions. And what do these regions do?
Well, the regions that grew were those that are specifically associated with social decision-making and empathy (mid-superior temporal sulcus and ventral-dysgranular insula, if you’re interested).
So, in short, or a more correct headline, is that socialising grows the regions of your brain that are involved in social decision making and empathy.
Probably no bad thing to have!
Reference:
Camille Testard, Lauren J. N. Brent, Jesper Andersson, et al.
Social connections predict brain structure in a multidimensional free-ranging primate society.
Science Advances, 2022; 8 (15)
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl5794
More Quick Hits
Art Engages the Social brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences reported in last week’s Quick Hits on how engaging in the arts has a relationship with self-control and avoidance of disagreeable and criminal behaviour and that is why this...
Swearing can increase strength, self-confidence, and risky behaviour
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences wearing is frowned upon in many circumstances but is also used by many people in casual situations and particularly by comedians. So why do we swear if it is taboo? A team of...
Neurons for alcohol withdrawal
I’ve reported on alcohol a number of times. Most recently reporting that even low quantities of alcohol appear to age the brain (however, higher quantities are much worse). Researchers had previously found that a signalling molecule pathway in the brain seemed to...
How the Arts Help Self Control
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciencesome people criticise arts education, thinking that it is more play and has no clear life function. Normally a certain type of conservative. This is short minded; we know that arts...
How the gut communicates with your brain
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ust after publishing the article on Serotonin and stating that the gut and brain’s serotonin systems can be considered separate entities, out comes a piece of research to show that...
Are you an “elite sleeper”? It’s in your genes.
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences ’ve reported many times on different aspects of sleep and how important this is for health in general and for brain health in particular. You can go here for a short review of all...
Controlling social mingling by laser
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences here has been plenty of research into brain areas that contribute to our social brain but these researchers around Stephen Mague at Duke University went a step, or two, further and...
Exercise is Infectious
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences his is an older study (2017) I came across and found fascinating. As many of you regular readers will know I have reported many times on the benefits of exercise. But this study was...
Breastfeeding Improves Mother’s Cognitive Abilities — Years Later
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences o are you saying that breast feeding is not only good for the infant but also the mother?!Yes, we’ve know for a long, long time that breastfeeding is very good for the infant. Over...
Mothers Can Pass on Stress to Future Generations
Quick HitsDaily brief research updates from the cognitive sciences presume you’re not just talking about stressed mothers stressing out their kids and/or grandchildren?Not precisely. I’m talking about passing on stress activation patterns in DNA...